Both Ubuntu and Mac OS X come with pre-installed VNC solutions. The vino package in Ubuntu is a VNC server for GNOME. To enable screen sharing one can start Desktop Sharing Preferences and enable an option to allow other users to view desktop.
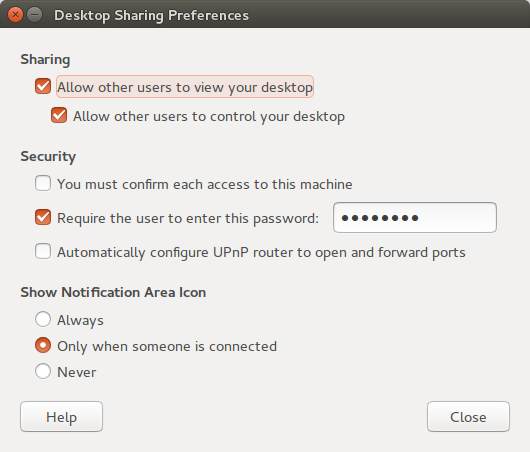
If you are using a Mac on the same network your Linux system should appear in the Shared tab in the Finder.
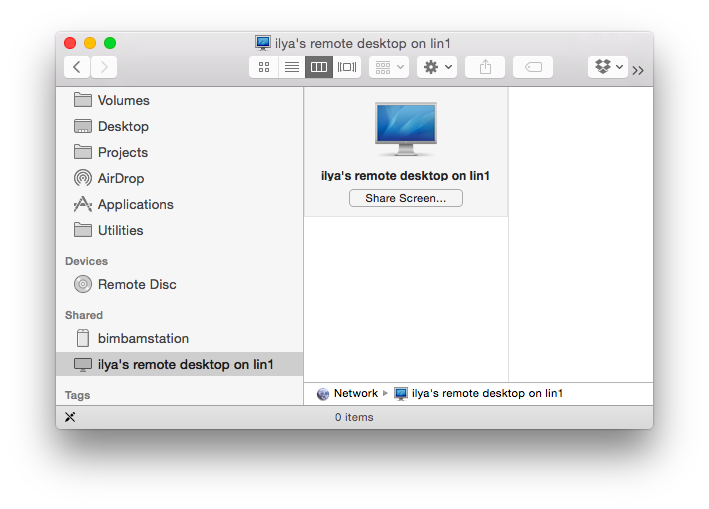
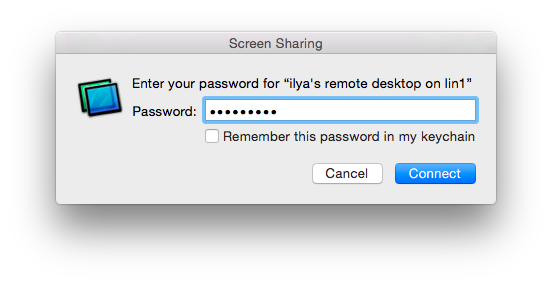
Clicking on Share Screen will invoke Mac’s VNC utility and prompt for the password.
If the connection fails
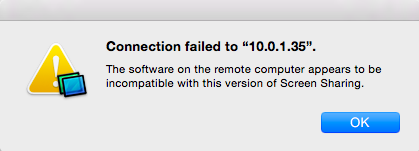
you might need to disable encryption on the server (Ubuntu) side by running the following command.
ilya@lin1:~$ gsettings set org.gnome.Vino require-encryption falseThere other ways to invoke Share Screen in Mac OS. You can do it directly from the terminal with
$ open /System/Library/CoreServices/Applications/Screen\ Sharing.appor you can open an XTerm and start a VNC session from it specifying the IP address and port of the target system.
$ open vnc://10.0.1.35:5900If the connection is successful and you can view and control your Ubuntu desktop on the Mac you can add
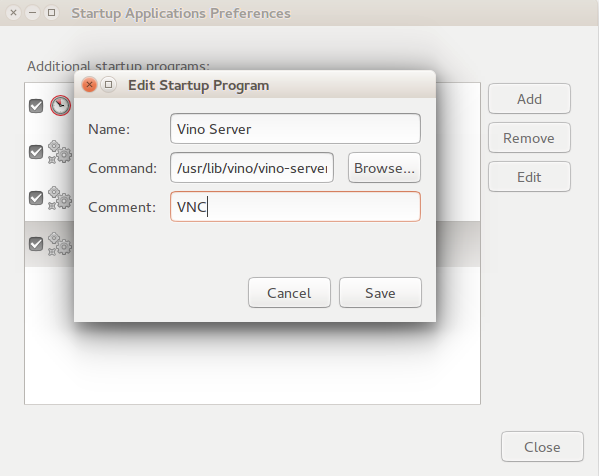
/usr/lib/vino/vino-servercommand to you Startup Applications.
Of course for pure command line access one can just ssh into the Linux system. To allow ssh access on the default port 22:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
$ sudo ufw allow 22To make the setup more secure one can follow recommendations of thepcspy.com to install fail2ban:
$ sudo apt-get install fail2banand change the port setting from the default to some value in the 10,000-64,000 range. To do that change the line “Port 22” in /etc/ssh/sshd_config to the chosen value and run restart the server.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restartOnce that is done, you can connect to the right port with
$ ssh -p 12345 yourname@10.0.1.35